What is DRM Protected Content? Definition, How It Works
What is DRM-protected content? In this blog, we delve into the workings of DRM and its role in safeguarding intellectual property.
The internet continues to be an excellent platform for sharing and promoting creativity, but it comes with inherent risks. Content creators often prefer not to have their work freely distributed, as it can lead to piracy and copyright infringement. This article explores DRM protection and its role in safeguarding your work and that of others.
What is DRM Protected Content?
Content under DRM protection comes with specific limitations on its usage.
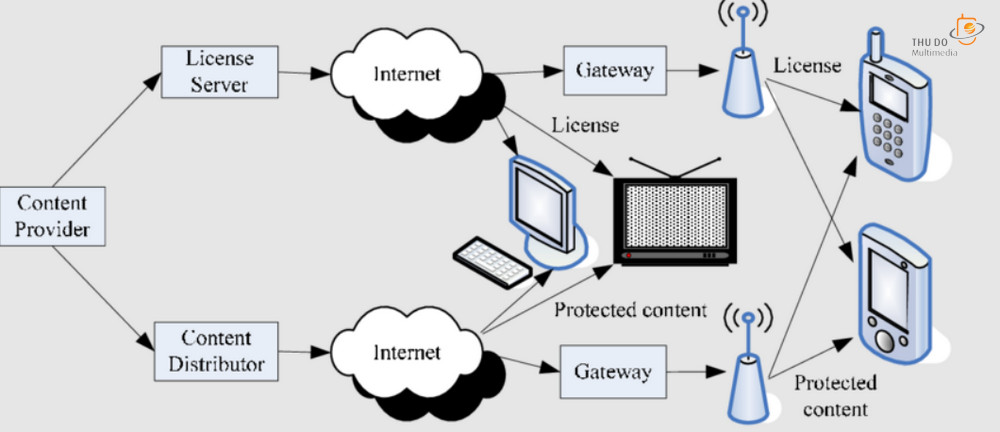
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is responsible for managing the authorization and usage of copyrighted material, spanning various forms such as movies, music, books, shows, games, and other digital assets. Authentication is a prerequisite for utilizing DRM-protected content; for instance, individuals seeking to copy a specific DRM-protected file may need to provide their username and password.
Media files may be subject to various DRM restrictions. The level of complexity in DRM protection is determined by the content creator, as it is encoded into the protected file. For instance, a content creator might restrict their media file to play only a limited number of times on a device. Alternatively, they may specify that the file can only be played on a particular application.
Additional forms of DRM protection may require users to input a password before copying or editing a file.
Understanding the mechanics of DRM provides insight into its operation.
The DRM protection process comprises four primary stages.
- Encryption: To safeguard the content, encryption renders it unusable if accessed without proper authorization, as it remains scrambled until decrypted.
- Management: Rules governing the encryption key restrict access, ensuring that not everyone can obtain it.
- Authorization: User verification, commonly through a username and password, is mandatory to confirm the user’s eligibility for obtaining the key.
- Regular Verification: Periodic verification of user authorization ensures that they maintain the right to hold the key.
Fundamentally, this is the process when accessing DRM-protected content:
Encryption is applied to the digital content.
- The key is linked to a digital license outlining usage rules for the content.
- Upon a user’s access request, the DRM client authenticates them and provides the appropriate key.
- The key is utilized to decrypt the content, allowing the user to view it.

What are the Rules of DRM?”
Earlier, we discussed that the DRM license outlines specific rules and prerequisites for granting access to a designated user. Below, we’ll explore some of the regulations embedded within the license:
- Verification of the user subscription is the first step.
- Validating the content access location is the second consideration.
- Determining the allowable simultaneous devices for content display is the third aspect.
- Establishing the maximum viewing hours per user is the fourth rule.
Upon initiating playback of a movie or show on a DRM-protected platform, the DRM client systematically examines each rule within the license. If all criteria are met, the content is then allowed to play.
Examples of content safeguarded by DRM measures.
Streaming or hosting services exemplify the implementation of DRM for content protection, allowing content creators to monetize their work on secured websites. Various applications of DRM comprise:
Online video players restrict file downloads, enabling users to watch videos within the browser or app by logging in with their credentials.
Video games require users to input a unique registration code obtained from the website during installation.
Music players in the online domain may prohibit file downloads, and if permitted, the downloaded file is typically encrypted to deter copying onto other devices.
As an illustration, Spotify incorporates DRM into its platform. Although users can download digital libraries, it’s uncommon for them to do so. Even if someone downloads the files, playing them on a different device poses challenges. Conversely, streaming music directly from Spotify is seamless, allowing the platform to safeguard its content and compensate content creators.
- Advantages of Implementing DRM for Content Protection
- Empowering content creators with the ability to determine the fate of their content, DRM provides numerous benefits, including:
- Safeguarding revenue streams for content creators
- Thwarting unauthorized use or sharing of digital content
- Implementing varied levels of access control based on user preferences

Combating plagiarization and piracy
DRM operates seamlessly without user intervention, and it enjoys compatibility with various devices, set-top boxes, and web browsers. The primary DRM platforms, namely Google Widevine, Apple FairPlay, and MS PlayReady handle decryption in the background, ensuring that users are not privy to the specific DRM service utilized.
From the user’s perspective, the process unfolds seamlessly. In contrast, consider the Sony rootkit incident in 2005, where the installation of “security software” on their discs not only hindered users from burning CDs but also facilitated malware infiltration into their PCs, causing a significant scandal. In comparison, DRM stands out as a superior method for safeguarding intellectual property.
While DRM serves to safeguard a creator’s work, it cannot eradicate piracy. For instance, another device can capture the screen displaying a video, resulting in a new, non-DRM-protected video file susceptible to illegal copying and sharing. Nevertheless, DRM significantly mitigates piracy.
Summarize
Enabling content creators and distributors to safeguard their intellectual property, DRM is commonly implemented across various mediums, including:
- Music
- Movies
- Books
- Images
Through content protection, DRM minimizes the threat of both piracy and copyright theft, thus averting potential income loss. To learn more information about DRM. For solutions to protect digital content copyright, readers can refer to and see the website: thudomultimedia.com. For quick, direct consulting support.

Recent Comments